Mouse anti-Human NGAL Monoclonal Antibody | anti-NGAL antibody
NGAL Antibody
IHC: 1:50-1:200
ICC: 1:50-1:200
ICC (Immunocytochemistry)
(ICC staining NGAL in SW480 cells (red). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue).Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.)
ICC (Immunocytochemistry)
(ICC staining NGAL in NIH-3T3 cells (red). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.)
ICC (Immunocytochemistry)
(ICC staining NGAL in A431 cells (red). The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.)
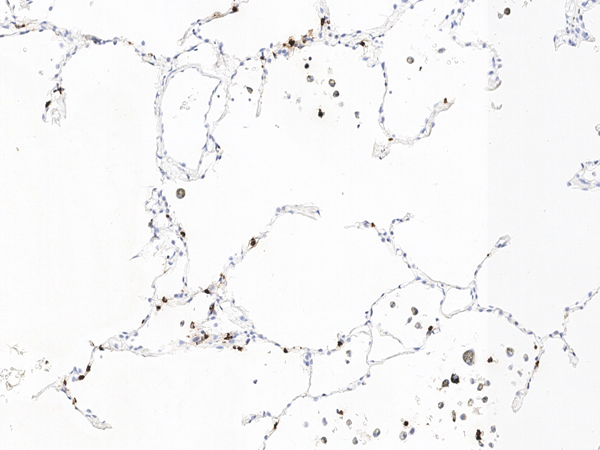
IHC (Immunohistochemistry)
(Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded huamn liver tissue using anti-NGAL antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.)
IHC (Immunohistochemistry)
(Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human stomach cancer tissue using anti-NGAL antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.)
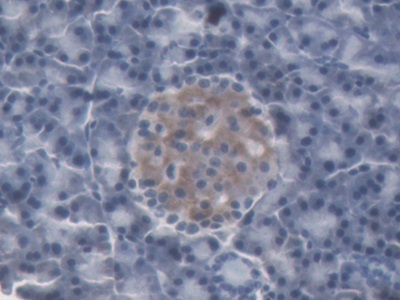
IHC (Immunohistochemistry)
(Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human spleen tissue using anti-NGAL Tubulin antibody. Counter stained with hematoxylin.)
NCBI and Uniprot Product Information
Similar Products
Product Notes
The NGAL lcn2 (Catalog #AAA29895) is an Antibody produced from Mouse and is intended for research purposes only. The product is available for immediate purchase. The NGAL Antibody reacts with Human and may cross-react with other species as described in the data sheet. AAA Biotech's NGAL can be used in a range of immunoassay formats including, but not limited to, WB (Western Blot), ICC (Immunocytochemistry), IHC (Immunohistochemistry). WB: 1:1000 IHC: 1:50-1:200 ICC: 1:50-1:200. Researchers should empirically determine the suitability of the NGAL lcn2 for an application not listed in the data sheet. Researchers commonly develop new applications and it is an integral, important part of the investigative research process. It is sometimes possible for the material contained within the vial of "NGAL, Monoclonal Antibody" to become dispersed throughout the inside of the vial, particularly around the seal of said vial, during shipment and storage. We always suggest centrifuging these vials to consolidate all of the liquid away from the lid and to the bottom of the vial prior to opening. Please be advised that certain products may require dry ice for shipping and that, if this is the case, an additional dry ice fee may also be required.Precautions
All products in the AAA Biotech catalog are strictly for research-use only, and are absolutely not suitable for use in any sort of medical, therapeutic, prophylactic, in-vivo, or diagnostic capacity. By purchasing a product from AAA Biotech, you are explicitly certifying that said products will be properly tested and used in line with industry standard. AAA Biotech and its authorized distribution partners reserve the right to refuse to fulfill any order if we have any indication that a purchaser may be intending to use a product outside of our accepted criteria.Disclaimer
Though we do strive to guarantee the information represented in this datasheet, AAA Biotech cannot be held responsible for any oversights or imprecisions. AAA Biotech reserves the right to adjust any aspect of this datasheet at any time and without notice. It is the responsibility of the customer to inform AAA Biotech of any product performance issues observed or experienced within 30 days of receipt of said product. To see additional details on this or any of our other policies, please see our Terms & Conditions page.Frequently Asked Questions
What is NGAL (Lipocalin‑2) and why is it important in human studies?
NGAL (neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin/lipocalin-2) is a 25 kDa protein that binds bacterial siderophores and mammalian iron-containing compounds. Originally identified in neutrophil granules, NGAL is now recognized as an early biomarker for acute kidney injury (AKI). NGAL rises rapidly in serum/urine (within 2 hours of kidney injury), preceding creatinine elevation by days. Its iron-sequestering role limits bacterial growth during infection; kidney injury increases tubular cell NGAL synthesis. NGAL's dual role—innate immunity and kidney damage indicator—makes it clinically important.
Can this NGAL antibody be used to detect elevated NGAL in kidney injury models?
Yes, NGAL antibodies effectively detect elevated NGAL in kidney injury models. Immunofluorescence on kidney sections shows NGAL accumulation in proximal tubular cells (sites of injury). Western blots quantify monomeric NGAL (~25 kDa); ELISA sandwich assays measure total serum/urine NGAL. In experimental AKI models (ischemia-reperfusion, nephrotoxins), NGAL rises 10-100 fold within hours. NGAL detection in urine/serum serves as an early AKI predictor before functional changes occur, enabling timely clinical intervention.
Is NGAL expression associated with inflammation or infection responses?
Yes, NGAL is a key inflammatory response protein. Activated neutrophils secrete dimeric NGAL; injured kidney tubular cells release monomeric NGAL. NGAL increases in bacterial infections (sepsis), where it contributes to innate immunity by sequestering iron-containing bacterial siderophores, limiting pathogenic growth. However, NGAL elevation in septic AKI reflects both kidney injury and inflammatory response; distinguishing sources (kidney vs. neutrophil) by oligomerization state helps clarify etiology. Inflammation is NGAL's confounding factor in AKI diagnostics.
Can this antibody be used for immunofluorescence, IHC, or Western blot?
Yes, NGAL antibodies are validated for all three applications. Immunofluorescence marks NGAL in kidney tubular cells, revealing injury localization and distribution. IHC on paraffin-embedded kidney biopsies shows cytoplasmic NGAL accumulation in diseased tubules. Western blots detect NGAL monomer (25 kDa) and dimeric forms (~50 kDa) after SDS-PAGE; non-reducing gels preserve physiological oligomerization. ELISA sandwich formats use two antibodies recognizing different NGAL epitopes, enabling sensitive quantification suitable for clinical diagnostics.
What sample types (serum, tissue, urine) work best for NGAL detection?
Urine NGAL is optimal for non-invasive AKI detection; it rises dramatically (>100-fold) within 2-6 hours post-injury, preceding serum creatinine changes. Plasma/serum NGAL also increases early but shows greater background variation (baseline elevation in inflammation). Kidney tissue immunofluorescence directly visualizes injury sites but requires biopsy. For clinical screening: urine NGAL (non-invasive, early detection); for monitoring: plasma NGAL (accessible); tissue IF (confirming injury localization). AAA Biotech antibodies optimize each sample type.
Is NGAL commonly studied as a biomarker for acute kidney injury or cancer?
NGAL is extensively studied as an AKI biomarker - its predictive value (AUC 0.86-0.93) surpasses creatinine. Clinical applications: post-operative AKI prediction, sepsis-associated AKI, dialysis requirement forecasting. Cancer relevance: NGAL promotes tumor cell survival and is elevated in various malignancies (ovarian, prostate, and gastric cancers), correlating with poor prognosis. NGAL contributes to tumor progression through growth factor signaling. Dual biomarker status (AKI and cancer) makes NGAL valuable for multi-purpose clinical research and diagnostics.
Item has been added to Shopping Cart
If you are ready to order, navigate to Shopping Cart and get ready to checkout.